27 16 As A Mixed Number
News Co
May 08, 2025 · 4 min read
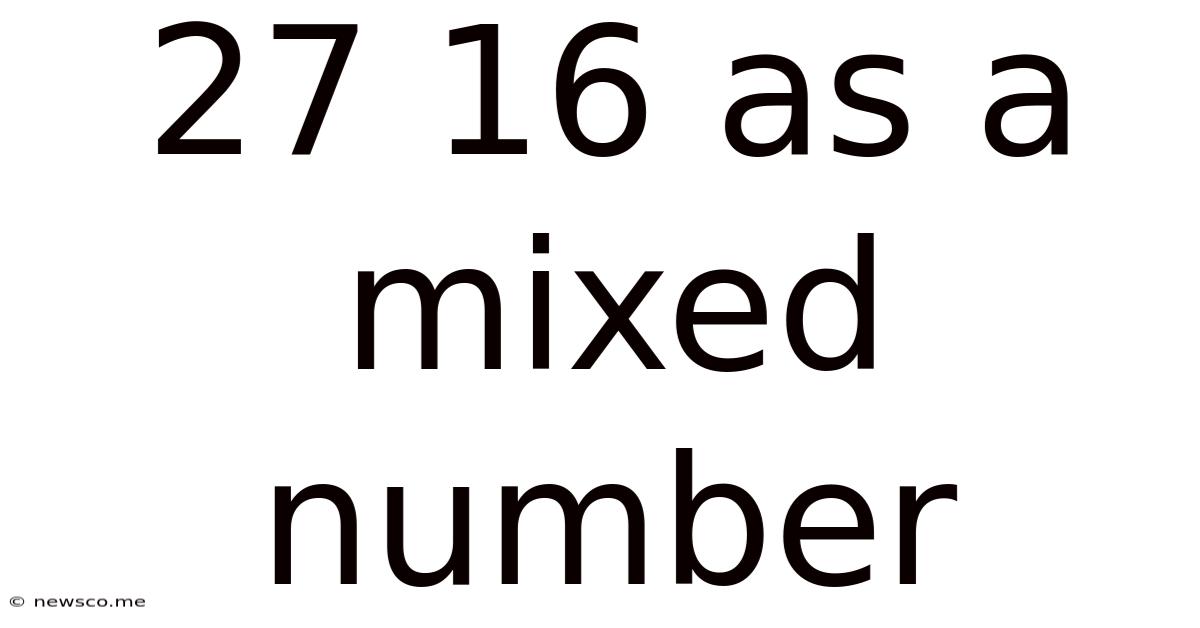
Table of Contents
27/16 as a Mixed Number: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding fractions and their conversion to mixed numbers is a fundamental skill in mathematics. This comprehensive guide will delve into the process of converting the improper fraction 27/16 into a mixed number, explaining the concept in detail and providing practical examples to solidify your understanding. We'll also explore the broader context of fractions and mixed numbers, their applications, and how to perform various operations with them.
What is a Mixed Number?
A mixed number combines a whole number and a proper fraction. A proper fraction is one where the numerator (the top number) is smaller than the denominator (the bottom number). For example, 1 ¾, 2 ⅔, and 3 ⅛ are all mixed numbers. They represent a quantity that's greater than one whole unit.
What is an Improper Fraction?
An improper fraction, on the other hand, is a fraction where the numerator is greater than or equal to the denominator. Examples include 7/4, 11/5, and, in our case, 27/16. Improper fractions represent a quantity greater than or equal to one whole unit.
Converting 27/16 to a Mixed Number: The Process
The process of converting an improper fraction like 27/16 to a mixed number involves dividing the numerator by the denominator. Here's a step-by-step breakdown:
-
Divide the numerator by the denominator: We divide 27 by 16.
27 ÷ 16 = 1 with a remainder of 11
-
The quotient becomes the whole number: The result of the division (1) becomes the whole number part of our mixed number.
-
The remainder becomes the numerator: The remainder (11) becomes the numerator of the fractional part.
-
The denominator stays the same: The denominator of the improper fraction (16) remains unchanged in the mixed number.
Therefore, 27/16 as a mixed number is 1 11/16.
Visualizing the Conversion
Imagine you have 27 slices of pizza, and each pizza has 16 slices. You can assemble 1 whole pizza (16 slices) and have 11 slices left over. This visually represents the mixed number 1 11/16.
Why Convert to Mixed Numbers?
While improper fractions are perfectly valid representations, mixed numbers are often preferred for several reasons:
-
Easier to understand: Mixed numbers offer a more intuitive way to grasp the magnitude of a quantity. It's generally easier to visualize 1 11/16 pizzas than 27/16 pizzas.
-
Simpler in practical applications: In real-world scenarios, particularly involving measurements or quantities, mixed numbers are more commonly used and understood. For example, it's more natural to say "1 and 11/16 inches" than "27/16 inches."
-
Facilitates calculations: In some calculations, particularly addition and subtraction of fractions, using mixed numbers can be simpler than working solely with improper fractions.
Further Exploration of Fractions and Mixed Numbers
Adding and Subtracting Fractions and Mixed Numbers:
To add or subtract fractions (including those within mixed numbers), they must share a common denominator. If the denominators are different, you need to find the least common multiple (LCM) and adjust the fractions accordingly.
Example (Addition):
1 ½ + 2 ⅓
First, convert to improper fractions: (3/2) + (7/3)
Find the LCM of 2 and 3 (which is 6):
(9/6) + (14/6) = 23/6
Convert back to a mixed number: 3 ⁵/₆
Example (Subtraction):
3 ¼ - 1 ⅔
Convert to improper fractions: (13/4) - (5/3)
Find the LCM of 4 and 3 (which is 12):
(39/12) - (20/12) = 19/12
Convert back to a mixed number: 1 ⁷/₁₂
Multiplying and Dividing Fractions and Mixed Numbers:
Multiplication and division with mixed numbers involve a slightly different approach. It's generally easier to convert mixed numbers into improper fractions before performing these operations.
Example (Multiplication):
1 ½ x 2 ⅓ = (3/2) x (7/3) = 21/6 = 7/2 = 3 ½
Example (Division):
2 ¾ ÷ 1 ½ = (11/4) ÷ (3/2) = (11/4) x (2/3) = 22/12 = 11/6 = 1 ⁵/₆
Real-World Applications
The conversion of improper fractions to mixed numbers, and the manipulation of fractions and mixed numbers in general, has numerous practical applications in everyday life, including:
-
Cooking and Baking: Recipes often involve fractional measurements, and understanding how to work with fractions is essential for accurate results.
-
Construction and Engineering: Precise measurements are critical in these fields, demanding a strong understanding of fractions and mixed numbers.
-
Finance: Calculating interest rates, discounts, and other financial aspects frequently involves working with fractions.
-
Data Analysis: Representing and interpreting data often requires working with fractions and percentages (which are closely related to fractions).
Conclusion
Converting 27/16 to the mixed number 1 11/16 is a straightforward process, but mastering this skill opens the door to a deeper understanding of fractions and their significant role in various mathematical applications and real-world scenarios. Understanding how to convert between improper fractions and mixed numbers, and how to perform arithmetic operations with these forms, is crucial for success in mathematics and many related fields. This guide provides a strong foundation for tackling more complex fraction-related problems and strengthening your overall mathematical abilities. Remember to practice regularly to build proficiency and confidence in working with fractions and mixed numbers. By consistently applying these techniques, you'll enhance your problem-solving skills and develop a more intuitive understanding of numerical quantities.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 27 16 As A Mixed Number . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.