How Much Is 50 Degrees Fahrenheit In Celsius
News Co
Apr 05, 2025 · 5 min read
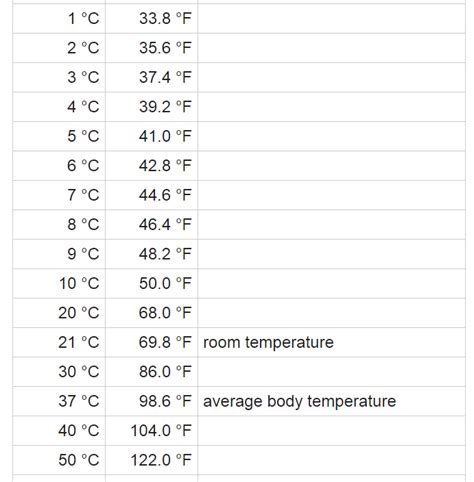
Table of Contents
How Much is 50 Degrees Fahrenheit in Celsius? A Comprehensive Guide
The question, "How much is 50 degrees Fahrenheit in Celsius?" might seem simple, but it opens a door to understanding temperature conversions, their significance, and the broader context of temperature measurement. This comprehensive guide will not only answer the question directly but delve into the intricacies of the Fahrenheit and Celsius scales, offering practical applications and insights for everyone from casual users to science enthusiasts.
Understanding Fahrenheit and Celsius
Before we dive into the conversion, let's grasp the fundamental differences between these two widely used temperature scales.
Fahrenheit (°F): A Brief History
Developed by Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit in the early 18th century, the Fahrenheit scale originally used a zero point based on a brine solution's freezing point. Over time, the scale was redefined, with 32°F representing the freezing point of water and 212°F its boiling point, at standard atmospheric pressure. The Fahrenheit scale is still predominantly used in the United States, its territories, and a few other countries.
Celsius (°C): The Metric Standard
The Celsius scale, also known as the centigrade scale, is the primary temperature scale used worldwide. Anders Celsius, a Swedish astronomer, introduced a reversed version of the scale in the 1740s. It sets 0°C as the freezing point of water and 100°C as its boiling point, again at standard atmospheric pressure. The Celsius scale is part of the International System of Units (SI), making it the preferred scale for scientific work and most international contexts.
Converting 50°F to Celsius: The Calculation
The conversion from Fahrenheit to Celsius involves a straightforward formula:
°C = (°F - 32) × 5/9
Let's plug in 50°F:
°C = (50 - 32) × 5/9 = 18 × 5/9 = 10
Therefore, 50 degrees Fahrenheit is equal to 10 degrees Celsius.
Beyond the Calculation: Practical Applications and Significance
While the conversion itself is simple, understanding the implications of 10°C is crucial. A temperature of 10°C (50°F) is generally considered mildly cool. Here are some practical applications and considerations:
Daily Life Applications:
- Clothing: In many parts of the world, 10°C would necessitate a light jacket or sweater, especially during the morning and evening.
- Outdoor Activities: It's a pleasant temperature for various outdoor activities like walking, cycling, or light hiking. However, if you are sensitive to cold, layers might still be necessary.
- Gardening: 10°C is generally favorable for many plants, although some might require protection from frost, depending on the plant species and specific climate conditions.
- Indoor Comfort: For most people, 10°C indoors might feel somewhat chilly, and central heating or other warming mechanisms would likely be used.
Scientific and Industrial Applications:
- Chemistry and Physics: In scientific experiments and industrial processes involving temperature-sensitive materials, precise conversions between Fahrenheit and Celsius are essential for accurate results and safety.
- Meteorology: While most weather reporting globally uses Celsius, understanding the equivalent Fahrenheit temperatures helps in comparing weather data from various sources.
- Food Processing: Temperature control is critical in food processing, and accurate conversions are crucial to maintaining quality and safety standards.
Temperature Conversions: A Deeper Dive
Understanding the conversion between Fahrenheit and Celsius extends beyond simply using the formula. It involves appreciating the relationship between the two scales and the underlying principles of temperature measurement.
Understanding the Linear Relationship:
The conversion formula reflects a linear relationship between the Fahrenheit and Celsius scales. This means that a constant change in Fahrenheit corresponds to a proportional change in Celsius. This linear relationship is key to understanding the interchangeability and equivalence of the two scales, even though their zero points and scaling differ significantly.
The Importance of Standard Atmospheric Pressure:
The conversion is accurate only under standard atmospheric pressure. At higher altitudes or different pressures, the boiling and freezing points of water will vary slightly, affecting the accuracy of the conversion. For high-precision work, adjustments for pressure must be made.
Other Temperature Scales: Kelvin
Besides Fahrenheit and Celsius, the Kelvin scale is another crucial temperature scale, particularly in scientific applications. Kelvin uses absolute zero (0 K) as its zero point, representing the theoretical point at which all molecular motion ceases. Conversions between Kelvin, Celsius, and Fahrenheit are possible and essential for scientific research.
The Kelvin scale is defined as:
K = °C + 273.15
Therefore, 10°C is equivalent to 283.15 K.
Advanced Concepts and Applications
The basic temperature conversion serves as a foundation for more advanced applications in various fields:
- Climate Science: Understanding and converting temperature data are critical in climate research, analyzing temperature trends, and predicting future climate changes.
- Medical Applications: Accurate temperature measurement is crucial in healthcare, monitoring patient body temperature, and administering appropriate treatments.
- Material Science: The behavior and properties of many materials are temperature-dependent, requiring accurate temperature conversions in their analysis and applications.
Troubleshooting and Common Mistakes
While the conversion is relatively straightforward, some common errors can occur:
- Order of Operations: Ensure you subtract 32 from the Fahrenheit temperature before multiplying by 5/9. Incorrect order of operations will lead to an inaccurate result.
- Unit Errors: Always double-check your units to ensure you are working with Fahrenheit and not Celsius. Mistakes in units can propagate throughout calculations.
- Rounding Errors: Depending on the level of precision required, rounding off numbers in intermediate steps might introduce inaccuracies. For high-precision applications, it's advisable to avoid rounding off until the final result.
Conclusion: Mastering Temperature Conversions
Understanding how to convert 50°F to Celsius (and vice versa) is a fundamental skill with broad applications. While the calculation is simple, this guide emphasizes the deeper understanding of the Fahrenheit and Celsius scales, their relationships, and their importance in various fields. Mastering temperature conversions contributes to a more informed understanding of the physical world and enhances problem-solving capabilities across diverse domains. From everyday life to scientific research, the ability to accurately convert between temperature scales is invaluable. Beyond the simple mathematical operation, it represents a deeper appreciation for the measurement of temperature and its significance in our world.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Much Is 50 Degrees Fahrenheit In Celsius . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.