What Is 59 In Roman Numerals
News Co
Apr 05, 2025 · 5 min read
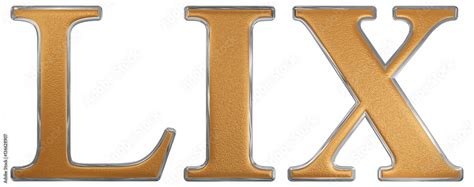
Table of Contents
What is 59 in Roman Numerals? A Deep Dive into Roman Numeral Systems
The question, "What is 59 in Roman numerals?" might seem simple at first glance. However, understanding the answer fully requires delving into the fascinating history and intricacies of the Roman numeral system. This article will not only answer that question but also provide a comprehensive overview of Roman numerals, exploring their origins, rules, and applications, even touching on their limitations and why they were eventually superseded by the Hindu-Arabic numeral system we use today.
Understanding Roman Numerals: A Brief History
Roman numerals, a system of numerical notation used by the ancient Romans, are based on combinations of seven basic symbols:
- I: 1
- V: 5
- X: 10
- L: 50
- C: 100
- D: 500
- M: 1000
These symbols, representing different powers of ten and their halfway points, are combined to create numbers. The system's origins are debated, with some theories suggesting Etruscan influence. Regardless of their precise origins, Roman numerals were used extensively in various aspects of Roman life, from recording dates and measurements to marking milestones and monumental inscriptions. Their longevity is a testament to their efficacy, even if they possess inherent limitations.
The Mechanics of Roman Numeral Construction
The core principle of Roman numerals lies in additive and subtractive notation. This means that smaller values preceding larger values are subtracted, while smaller values following larger values are added.
Additive Notation: For example, XVI (16) is formed by adding X (10), V (5), and I (1): 10 + 5 + 1 = 16. Similarly, LXXXVIII (88) is calculated as L (50) + XXX (30) + VIII (8) = 88.
Subtractive Notation: This is where things get slightly more complex. Subtraction is only used in specific cases involving the following pairs:
- IV: 4 (5 - 1)
- IX: 9 (10 - 1)
- XL: 40 (50 - 10)
- XC: 90 (100 - 10)
- CD: 400 (500 - 100)
- CM: 900 (1000 - 100)
These subtractive combinations significantly improve the system's efficiency, avoiding overly long strings of symbols. For instance, representing 99 as LXXXXVIIII is less elegant than XCIX.
The Importance of Placement:
The placement of the symbols is crucial. A smaller value placed before a larger value indicates subtraction; otherwise, it's addition. VI is 6 (5 + 1), but IV is 4 (5 - 1). This positional dependence is a key feature differentiating Roman numerals from positional systems like the Hindu-Arabic system.
So, What is 59 in Roman Numerals?
Now, armed with this knowledge, we can easily determine the Roman numeral representation of 59. We can break it down as follows:
59 = 50 + 9
We know that 50 is represented by L, and 9 is represented by IX (10 - 1). Therefore, 59 in Roman numerals is LIX.
Beyond the Basics: Advanced Roman Numeral Concepts
While the basics of Roman numerals are relatively simple, there are some nuances to be aware of:
-
No Zero: The Roman numeral system lacks a symbol for zero. This absence significantly impacted its mathematical capabilities compared to later systems that incorporated zero.
-
Limited Representation of Large Numbers: While large numbers could be represented, they became cumbersome and difficult to read with an increase in magnitude. The system relies on repetition, making it inefficient for very large figures.
-
Variations and inconsistencies: Over time, different variations and styles of Roman numerals emerged. While the core symbols remained consistent, their exact forms sometimes differed based on the era and the context in which they were used.
-
Bar Notation: For representing very large numbers, a bar placed above a numeral multiplied its value by 1000. For example,
\overline{X}represents 10,000.
The Decline of Roman Numerals and the Rise of Hindu-Arabic Numerals
Despite their widespread use for centuries, Roman numerals eventually gave way to the Hindu-Arabic numeral system. The Hindu-Arabic system, with its positional notation and the inclusion of zero, offered significant advantages in terms of efficiency and complexity of mathematical operations. The Hindu-Arabic system could handle arithmetic operations like multiplication and division far more easily, a key factor in its widespread adoption.
The transition was gradual, but by the late Middle Ages, the Hindu-Arabic system was gaining prominence, particularly in scientific and commercial contexts where precise calculations were essential. Even today, Roman numerals persist in some specific contexts, primarily for stylistic purposes (like chapter numbering in books or on clock faces), showcasing their enduring legacy, even if their role in everyday mathematical computations has diminished.
Applications of Roman Numerals Today
While not used for everyday arithmetic, Roman numerals remain present in various aspects of modern life:
-
Clocks and watches: Many analog clocks use Roman numerals to mark hours. This is primarily a stylistic choice, adding a touch of classical elegance.
-
Outlines and chapter numbering: Roman numerals can be found in book outlines and chapter numbering. This serves as a visually distinct method of organizing content.
-
Copyright dates: Sometimes, copyright dates use Roman numerals, often to give a slightly more formal appearance.
-
Monuments and buildings: You'll often see Roman numerals on buildings and monuments, especially those aiming for a classical aesthetic. This reflects the system's historical significance.
-
Regal or formal settings: The use of Roman numerals sometimes conveys a sense of formality and tradition in official or ceremonial contexts.
Conclusion: The Enduring Legacy of LIX (59)
The seemingly simple question, "What is 59 in Roman numerals?" serves as a gateway to exploring a rich history and fascinating system of numerical notation. While the Hindu-Arabic system has become the dominant system globally for arithmetic operations, the Roman numeral system continues to hold cultural and historical significance. Its enduring presence in various applications highlights its enduring legacy and visual appeal. Understanding Roman numerals provides a valuable perspective on the evolution of mathematical systems and offers a glimpse into the intellectual world of the ancient Romans. The elegance of LIX, representing 59, is a testament to this enduring legacy. The system, despite its limitations, effectively showcases a unique approach to numerical representation that has left its mark on history and continues to resonate in our modern world.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is 59 In Roman Numerals . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.