What Is 70 In Roman Numerals
News Co
Apr 23, 2025 · 5 min read
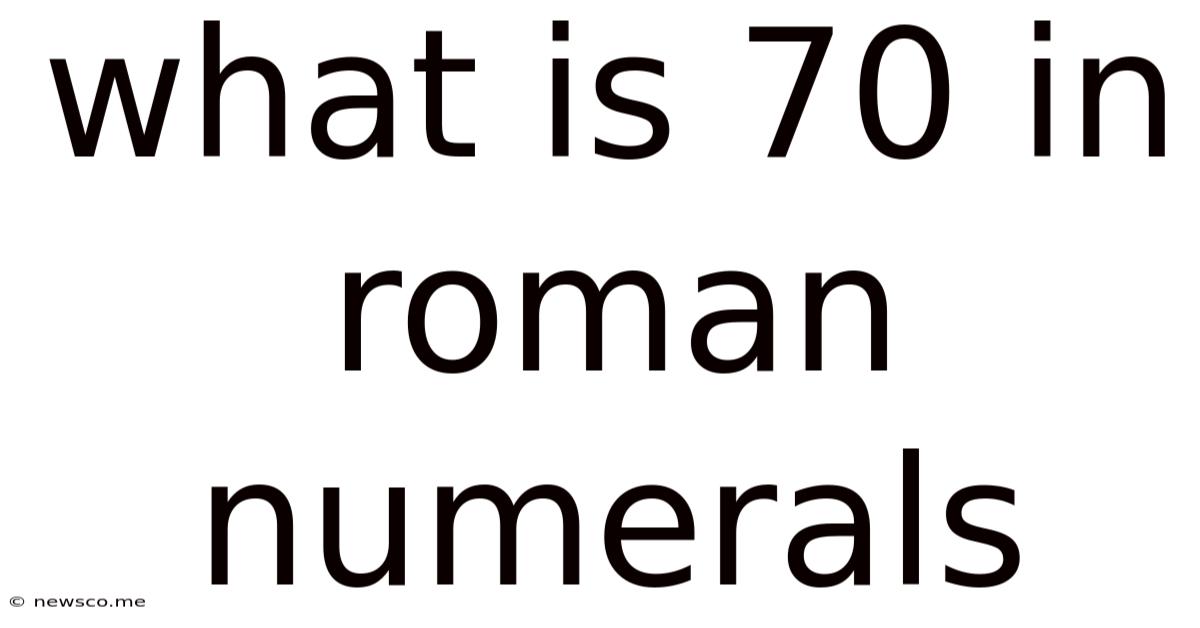
Table of Contents
What is 70 in Roman Numerals? A Deep Dive into Roman Numeration
The question, "What is 70 in Roman numerals?" seems simple enough. The answer, LXX, is readily available with a quick online search. However, understanding the why behind this answer opens a door to a fascinating world of ancient numeration systems and their enduring relevance. This article delves deep into the Roman numeral system, exploring its history, rules, and applications, culminating in a comprehensive understanding of how 70 is represented and the broader context of Roman numerals in modern society.
Understanding the Roman Numeral System
The Roman numeral system, developed in ancient Rome, utilizes a combination of seven letters to represent numbers: I (1), V (5), X (10), L (50), C (100), D (500), and M (1000). Unlike the decimal system we use today, which is based on a positional value (where the position of a digit determines its value), the Roman system relies on additive and subtractive principles.
Additive Principle
The additive principle is straightforward: smaller numerals placed to the right of a larger numeral are added to it. For instance:
- XI: X (10) + I (1) = 11
- LX: L (50) + X (10) = 60
- CL: C (100) + L (50) = 150
This principle forms the backbone of many Roman numeral representations. Understanding this is crucial to grasping the construction of larger numbers.
Subtractive Principle
The subtractive principle introduces a layer of complexity and efficiency. This principle dictates that when a smaller numeral is placed to the left of a larger numeral, it is subtracted from the larger numeral. This is not arbitrary; it only applies to specific combinations:
- IV: I (1) placed before V (5) means 5 - 1 = 4
- IX: I (1) placed before X (10) means 10 - 1 = 9
- XL: X (10) placed before L (50) means 50 - 10 = 40
- XC: X (10) placed before C (100) means 100 - 10 = 90
- CD: C (100) placed before D (500) means 500 - 100 = 400
- CM: C (100) placed before M (1000) means 1000 - 100 = 900
It's crucial to remember that this subtractive principle is only applied to these specific combinations. You wouldn't, for example, write IIX for 8; the correct representation is VIII.
Deconstructing 70 in Roman Numerals: LXX
Now, armed with the additive and subtractive principles, let's break down 70 in Roman numerals: LXX.
This representation utilizes the additive principle exclusively. L represents 50, and each X represents 10. Therefore:
LXX = L (50) + X (10) + X (10) = 70
There is no subtractive element involved in representing 70. This makes it a relatively straightforward example compared to numbers like 4 (IV) or 9 (IX).
Beyond 70: Exploring Larger and Smaller Roman Numerals
While understanding 70 is a key stepping stone, exploring the range of Roman numerals further solidifies comprehension. Let's examine some examples:
- 39: XXXIX (30 + 9)
- 88: LXXXVIII (50 + 30 + 8)
- 1492: MCDXCII (1000 + 400 + 90 + 2)
- 1999: MCMXCIX (1000 + 900 + 90 + 9)
- 2024: MMXXIV (1000 + 1000 + 20 + 4)
These examples showcase the flexibility and, at times, the complexity of the Roman numeral system. Larger numbers often require a combination of both additive and subtractive principles for efficient representation.
The Historical Significance and Modern Uses of Roman Numerals
The Roman numeral system, while not as efficient as the decimal system for complex calculations, holds significant historical and cultural value. Its use dates back to ancient Rome and continued through the medieval period and beyond.
Historical Context
Roman numerals were integral to record-keeping, inscription on monuments, and everyday transactions in the Roman Empire. Their persistence is evident in various historical artifacts, from inscriptions on tombstones to documents detailing legal and financial matters.
Modern Applications
Despite the widespread adoption of the decimal system, Roman numerals remain relevant in modern society, though often for stylistic or symbolic purposes rather than mathematical calculations:
- Clock faces: Many clocks still utilize Roman numerals for their aesthetically pleasing appearance.
- Outlines and lists: Roman numerals are frequently used to organize outlines, chapters in books, or sequential lists.
- Copyright dates: You'll often see copyright dates expressed in Roman numerals (e.g., MMXXIII for 2023).
- Monarchs and Popes: The numbering of monarchs and popes frequently employs Roman numerals (e.g., King Henry VIII).
- Super Bowl: The annual Super Bowl is identified with Roman numerals (e.g., Super Bowl LVII).
These uses demonstrate the enduring legacy and cultural significance of the Roman numeral system, extending far beyond its original mathematical applications.
Common Mistakes and Misconceptions
While seemingly straightforward, there are some common mistakes people make when working with Roman numerals:
- Incorrect subtractive usage: As previously emphasized, the subtractive principle only applies to specific combinations (IV, IX, XL, XC, CD, CM). Improper application leads to incorrect representations.
- Repetition limitations: You can only repeat a numeral a maximum of three times consecutively (e.g., III, XXX, CCC). After that, you must use a different combination.
- Incorrect order: The numerals must be arranged in descending order of value, with the exception of the subtractive principle.
Conclusion: Mastering Roman Numerals
Understanding "what is 70 in Roman numerals" is more than simply memorizing LXX. It's about grasping the fundamental principles of the Roman numeral system, its historical context, and its continued relevance in modern society. By comprehending both the additive and subtractive principles, and recognizing the limitations and potential pitfalls, one can confidently navigate the intricacies of this ancient and enduring system of numeration. The enduring presence of Roman numerals underscores their cultural importance and their continued value as a unique and visually appealing method of representing numbers. They offer a tangible link to the past while finding unexpected applications in contemporary contexts.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is 70 In Roman Numerals . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.