What Is 80 Degrees In Celsius
News Co
Apr 01, 2025 · 5 min read
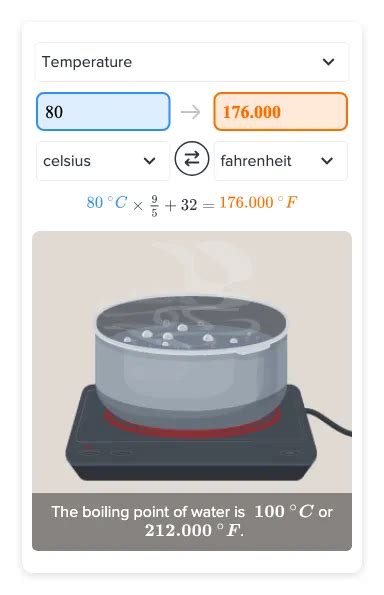
Table of Contents
What is 80 Degrees in Celsius? A Comprehensive Guide to Temperature Conversions and Applications
Knowing how to convert between different temperature scales is a crucial skill, especially in a globalized world where information and data often utilize various units of measurement. This comprehensive guide will delve into the question: "What is 80 degrees in Celsius?" We'll explore the conversion process, examine the significance of 80°C in various contexts, and discuss its implications in everyday life and various scientific applications.
Understanding Temperature Scales
Before we dive into the conversion, it's crucial to understand the different temperature scales commonly used: Celsius (°C), Fahrenheit (°F), and Kelvin (K).
-
Celsius (°C): Also known as the centigrade scale, Celsius is widely used globally and is based on the freezing and boiling points of water at standard atmospheric pressure. 0°C is the freezing point of water, and 100°C is its boiling point.
-
Fahrenheit (°F): Primarily used in the United States, Fahrenheit uses different reference points. 32°F is the freezing point of water, and 212°F is its boiling point.
-
Kelvin (K): Used primarily in scientific contexts, Kelvin is an absolute temperature scale. Zero Kelvin (0 K) represents absolute zero, the theoretical point at which all molecular motion ceases. There are no negative values in the Kelvin scale.
Converting 80 Degrees Celsius to Other Scales
Now, let's focus on converting 80°C to other scales. Understanding these conversions is vital for various applications, from cooking and baking to scientific research.
Converting 80°C to Fahrenheit (°F)
The formula to convert Celsius to Fahrenheit is:
°F = (°C × 9/5) + 32
Plugging in 80°C:
°F = (80 × 9/5) + 32 = 144 + 32 = 176°F
Therefore, 80°C is equivalent to 176°F.
Converting 80°C to Kelvin (K)
The formula to convert Celsius to Kelvin is:
K = °C + 273.15
Plugging in 80°C:
K = 80 + 273.15 = 353.15 K
Therefore, 80°C is equivalent to 353.15 K.
The Significance of 80°C in Different Contexts
80°C represents a significant temperature in various applications. Let's explore some key contexts:
Cooking and Food Safety
80°C is a crucial temperature in food preparation. While not the boiling point of water, it's high enough to:
-
Pasteurize food: Heating food to around 80°C for a specific duration can kill harmful bacteria and pathogens, enhancing food safety. This is particularly important for milk and other dairy products.
-
Cook certain dishes: Many recipes require temperatures around 80°C for optimal results. For instance, a low simmer for stews or sauces often falls within this range. Achieving consistent temperatures ensures even cooking and prevents burning.
-
Maintain food quality: Holding food at around 80°C in a bain-marie (a water bath) can help maintain its quality and temperature for extended periods, vital in catering or buffet settings.
Industrial Applications
80°C plays a role in various industrial processes:
-
Chemical reactions: Many chemical reactions require specific temperature ranges for optimal efficiency. 80°C might be the ideal temperature for certain chemical processes, ensuring desired outcomes without exceeding the safe operational limits of equipment.
-
Manufacturing processes: Certain industrial manufacturing processes necessitate temperatures around 80°C. For instance, some materials require heating to this temperature for molding or shaping.
-
Sterilization: In industrial settings, maintaining a temperature of around 80°C might be critical for sterilizing equipment or materials. This prevents contamination and ensures product quality.
Biological Applications
In biology and related fields, 80°C holds significance:
-
Enzyme activity: The optimal temperature range for many enzymes falls within a specific range. 80°C might be too high for some enzymes, leading to denaturation (loss of function). Conversely, some extremophile enzymes thrive at high temperatures.
-
DNA manipulation: Techniques like PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) involve heating DNA to specific temperatures. While 80°C isn't a primary temperature in PCR, maintaining a temperature around this range could be essential for specific steps.
-
Cell culture: Maintaining temperatures in the 80°C range is typically not suitable for cell culture, as it would lead to cell death.
Everyday Life
While we might not frequently measure temperatures in Celsius at home, 80°C is relevant in several everyday situations:
-
Hot showers: Many people prefer hot showers at temperatures around 40-45°C. 80°C is far too hot for a comfortable shower and could cause severe burns.
-
Ironing clothes: The ideal temperature for ironing varies depending on fabric type. While some fabrics might tolerate higher temperatures, 80°C is likely too high for most clothing items, leading to scorching or damage.
-
Boiling water: Boiling water reaches 100°C. Water at 80°C is very hot but not yet boiling. This distinction is important in certain cooking techniques and brewing tea or coffee.
Safety Considerations at 80°C
It's crucial to remember that 80°C is a high temperature and poses potential risks:
-
Burns: Direct contact with liquids or surfaces at 80°C can cause severe burns. Always exercise caution when handling hot materials.
-
Scalding: Steam generated from liquids at 80°C can also cause severe scalding. Avoid inhaling steam and ensure proper ventilation.
-
Equipment damage: Operating equipment at 80°C requires careful consideration of material compatibility and safety procedures. Always follow manufacturer instructions.
Conclusion: 80°C in a Broader Context
80 degrees Celsius is more than just a number; it's a temperature with implications across various fields. Understanding its conversion to other scales and its significance in cooking, industry, biology, and even everyday life underscores the importance of temperature measurement and control. While it's a relatively high temperature requiring caution, 80°C plays a vital role in numerous processes that impact our daily lives, from the food we eat to the products we use. Knowing what it means and how it affects different applications empowers us to utilize this knowledge safely and effectively. Remember always to prioritize safety when dealing with high temperatures.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is 80 Degrees In Celsius . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.