What Is A Shape Called With 11 Sides
News Co
Apr 03, 2025 · 5 min read
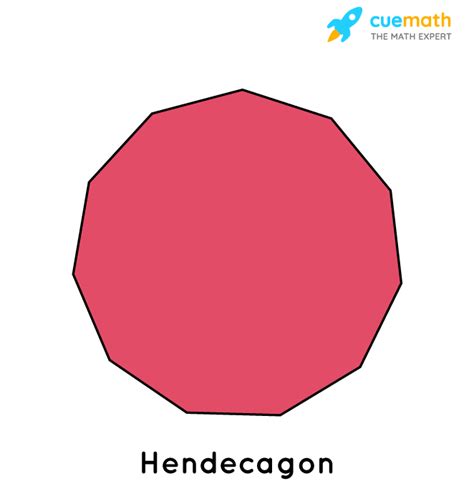
Table of Contents
What is a Shape Called with 11 Sides? Unlocking the World of Hendecagons
The world of geometry is filled with fascinating shapes, each with its own unique properties and names. While many of us are familiar with triangles, squares, and pentagons, some shapes remain shrouded in relative obscurity. Today, we delve into the intriguing realm of polygons with a specific focus on a shape with a less commonly known name: the hendecagon.
Understanding Polygons: A Foundation for Understanding Hendecagons
Before we dive deep into the specifics of a hendecagon, let's establish a solid foundation by understanding what polygons are. A polygon is a closed two-dimensional figure composed of straight line segments. These segments are called sides, and the points where the sides meet are called vertices or corners. Polygons are classified based on the number of sides they have.
- Triangles: 3 sides
- Quadrilaterals: 4 sides (squares, rectangles, rhombuses, etc., are all quadrilaterals)
- Pentagons: 5 sides
- Hexagons: 6 sides
- Heptagons: 7 sides
- Octagons: 8 sides
- Nonagons: 9 sides
- Decagons: 10 sides
- Undecagons/Hendecagons: 11 sides
- Dodecagons: 12 sides
And so on, with the number of sides increasing infinitely. As the number of sides increases, the polygon increasingly resembles a circle.
The Hendecagon: Unveiling the 11-Sided Shape
So, what is a shape with 11 sides called? It's called an hendecagon, also known as an undecagon. Both terms are perfectly acceptable and used interchangeably. The prefix "hendeca-" comes from the Greek word "hendeka," meaning eleven.
Understanding the properties of a hendecagon requires delving into the world of geometry. Let's explore some key characteristics:
Angles and Interior Angles of a Hendecagon
One of the most interesting aspects of any polygon is the sum of its interior angles. For any polygon with n sides, the sum of its interior angles can be calculated using the formula: (n - 2) * 180°.
For a hendecagon (n = 11), the sum of its interior angles is: (11 - 2) * 180° = 1620°. This means that the total of all the eleven interior angles in a hendecagon adds up to 1620 degrees.
To find the measure of each interior angle in a regular hendecagon (where all sides and angles are equal), we divide the sum of the interior angles by the number of sides: 1620° / 11 ≈ 147.27°. Therefore, each interior angle in a regular hendecagon measures approximately 147.27 degrees.
Exterior Angles of a Hendecagon
Exterior angles are the angles formed by extending one side of the polygon. The sum of the exterior angles of any polygon, regardless of the number of sides, is always 360°. In a regular hendecagon, each exterior angle measures 360° / 11 ≈ 32.73°.
Regular vs. Irregular Hendecagons
It's crucial to distinguish between regular and irregular hendecagons. A regular hendecagon has all its sides of equal length and all its angles of equal measure. An irregular hendecagon, on the other hand, has sides and angles of varying lengths and measures. The properties discussed above, such as the sum of interior angles and the measure of individual angles, apply specifically to regular hendecagons. Irregular hendecagons will have different angle measures, depending on the specific shape.
Hendecagons in the Real World: Unexpected Appearances
While not as commonly encountered as triangles or squares, hendecagons appear in various aspects of our world, often subtly:
Nature's Subtle Geometry
While not as prevalent as other polygons in naturally occurring structures, certain natural phenomena might exhibit approximate hendecagonal shapes. The arrangement of florets in some flowers or the patterns in certain crystals could, under specific conditions, loosely resemble a hendecagon. These natural occurrences are often approximations due to the complexities of biological and geological processes.
Design and Architecture
Architects and designers might incorporate hendecagons into their work, although it's not a frequently used shape. The unique properties of the hendecagon could be creatively employed for aesthetic or structural reasons in certain niche applications. The unusual number of sides can add an element of visual intrigue to a design.
Engineering and Technology
While less common than other polygons, the hendecagon could find applications in specific engineering and technological fields. For example, it might be relevant in the design of certain mechanical parts or in the development of specialized tools. The specific applications would be very niche and dependent on the exact requirements of the project.
Mathematical Exploration
Hendecagons play a role in mathematical exploration and problem-solving. Their properties provide opportunities for mathematical investigation and can serve as examples for broader geometric concepts.
Constructing a Hendecagon: A Challenging Task
Constructing a perfect regular hendecagon using only a compass and straightedge is impossible. This is because 11 is not a Fermat prime, a specific type of prime number that allows for the construction of regular polygons using only a compass and straightedge. However, approximate constructions can be achieved using various methods, including iterative techniques or employing specialized tools.
Exploring Further: Related Geometric Concepts
Understanding hendecagons opens doors to exploring further concepts within geometry:
- Star Polygons: By connecting every nth vertex of a hendecagon, different star polygons can be created. These fascinating shapes have a unique aesthetic appeal.
- Tessellations: While a regular hendecagon cannot tessellate (tile a plane without gaps or overlaps), irregular hendecagons could potentially be used in specific tessellations under particular configurations.
- Symmetry: A regular hendecagon possesses rotational symmetry of order 11. This means it can be rotated 11 times around its center before returning to its original position.
Conclusion: Appreciating the Hendecagon
The hendecagon, though less familiar than many other polygons, holds a significant place in the world of geometry. Understanding its properties, exploring its potential applications, and appreciating its unique characteristics enriches our understanding of mathematics and the world around us. While its rarity in everyday life might make it seem less important, its mathematical significance and potential for niche applications make it a fascinating and worthwhile subject of study. From the subtle geometries of nature to the potential applications in design and engineering, the hendecagon represents a small but significant piece of the vast and captivating puzzle of geometry. The next time you encounter an eleven-sided shape, you'll know precisely what it's called and appreciate its mathematical uniqueness.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Weeks In Four Months
Apr 04, 2025
-
28 Celsius Is What In Fahrenheit
Apr 04, 2025
-
9 To The Power Of 10
Apr 04, 2025
-
What Is The Lcm For 16 And 24
Apr 04, 2025
-
What Is 60 Percent Of 25
Apr 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is A Shape Called With 11 Sides . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
