What Is Li In Roman Numerals
News Co
Apr 03, 2025 · 5 min read
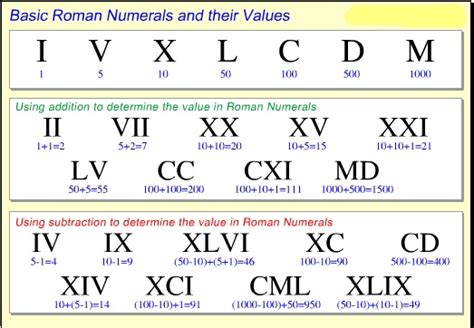
Table of Contents
What is LI in Roman Numerals? A Comprehensive Guide
Roman numerals, a system of numerical notation originating in ancient Rome, continue to hold relevance in various contexts today. From clock faces and chapter headings to copyright dates and outlines, understanding Roman numerals remains valuable. This comprehensive guide delves into the meaning of LI in Roman numerals, exploring the system's fundamental principles, common applications, and its historical significance.
Understanding the Roman Numeral System
The Roman numeral system uses combinations of seven letters to represent numbers:
- I: 1
- V: 5
- X: 10
- L: 50
- C: 100
- D: 500
- M: 1000
These letters are combined using a set of rules to create larger numbers. The core principle lies in additive and subtractive notation.
Additive Notation
In additive notation, the values of the symbols are added together. For example:
- VI: 6 (V + I = 5 + 1)
- XI: 11 (X + I = 10 + 1)
- LXV: 65 (L + X + V = 50 + 10 + 5)
Subtractive Notation
Subtractive notation utilizes the placement of smaller values before larger values to denote subtraction. This is crucial for efficient representation and avoids excessively long combinations. Common subtractive pairings include:
- IV: 4 (V - I = 5 - 1)
- IX: 9 (X - I = 10 - 1)
- XL: 40 (L - X = 50 - 10)
- XC: 90 (C - X = 100 - 10)
- CD: 400 (D - C = 500 - 100)
- CM: 900 (M - C = 1000 - 100)
Important Note: Subtractive notation only applies to specific pairings. You wouldn't write IIX for 8 (it should be VIII), or IIV for 3 (it should be III).
Deciphering LI: The Meaning
Now, let's address the specific question: What is LI in Roman numerals? Applying the additive principle, we find:
LI = L + I = 50 + 1 = 51
Therefore, LI represents the number 51 in Roman numerals.
Practical Applications of Roman Numerals: Beyond the Basics
While often associated with historical contexts, Roman numerals persist in modern usage for several reasons. Their continued presence showcases their enduring practicality and aesthetic appeal.
Timekeeping
Roman numerals are classically featured on analog clock faces, often indicating the hours. Their elegant appearance complements the design of traditional timepieces. While digital clocks dominate modern usage, the presence of Roman numerals on clocks adds a touch of sophistication.
Copyright Dates
Many books, films, and other creative works use Roman numerals for copyright dates, particularly when aiming for a more formal or traditional aesthetic. This adds a distinct visual touch, contributing to the overall presentation.
Outlines and Lists
Roman numerals provide a clear and visually organized structure for outlines and lists, particularly when nested sub-lists are involved. They allow for a hierarchical presentation that enhances readability and comprehension.
Monarchs and Popes
Historically and sometimes even currently, Roman numerals are used to differentiate between monarchs or Popes with the same name. This avoids confusion and establishes clear identification.
Architectural Designs
Roman numerals find application in architectural designs, often seen in building inscriptions or to indicate floor numbers in some buildings. The classic style adds to the architectural design’s aesthetic.
Chapter Numbering
Roman numerals continue to be used for chapter numbering in many books, adding a sense of tradition and formal presentation. This is especially true in academic texts and historical works.
Legal Documents
Roman numerals are occasionally used in legal documents for numbering sections or clauses, enhancing their formal and established tone.
The Historical Context of Roman Numerals
Understanding the historical context of Roman numerals adds another layer of appreciation for their significance. The system's origins can be traced back to ancient Rome, evolving over centuries. While its precise origins are debated among historians, the system's development reflects the Roman civilization's practices and needs.
The system's inherent limitations became apparent as larger numbers needed to be represented. The lack of a zero and the cumbersome nature of representing large numbers contributed to the eventual adoption of the more efficient Hindu-Arabic numeral system that we use predominantly today.
However, the Roman numeral system’s enduring presence highlights its aesthetic and practical appeal, even in a world dominated by the Hindu-Arabic system. The system’s persistence showcases a balance between practicality and cultural legacy.
Comparing Roman Numerals and Hindu-Arabic Numerals
Comparing the Roman numeral system with the Hindu-Arabic numeral system (the decimal system we commonly use) reveals key differences that highlight the strengths and weaknesses of each.
Hindu-Arabic Numerals:
- Place Value System: Employs a place-value system where the position of a digit determines its value. This allows for efficient representation of large numbers.
- Zero: Includes the concept of zero, crucial for representing place value and performing arithmetic operations effectively.
- Simplicity: Offers a simpler structure for calculations and larger numbers.
Roman Numerals:
- Additive/Subtractive: Relies on additive and subtractive notation, requiring memorization of symbol values and their combinations.
- No Zero: Lacks the concept of zero, limiting its use in complex arithmetic.
- Limited Efficiency: Can become cumbersome for representing very large numbers.
While Roman numerals lack the efficiency of the Hindu-Arabic system for complex calculations, their continued use illustrates their enduring appeal for certain applications. The historical and aesthetic value of Roman numerals justifies their continued presence in our modern world.
Advanced Applications and Nuances of Roman Numerals
For a deeper understanding, let’s explore some more advanced aspects of Roman numerals:
- Largest Number Representable: While theoretically, you could create arbitrarily large numbers, practical usage generally restricts numbers to a certain size. Very large numbers would be exceptionally cumbersome and difficult to read.
- Variations and Regional Differences: Subtle variations in Roman numeral notation exist across different historical periods and regions. While the core system is consistent, minor variations may be encountered in historical texts.
- Modern Interpretations: Modern interpretations often prioritize readability and clear understanding. While strict adherence to historical conventions may be relaxed in certain contexts, the core principles remain consistent.
Conclusion: The Enduring Legacy of LI and Roman Numerals
In conclusion, LI represents 51 in Roman numerals. This relatively simple number highlights the elegance and underlying principles of the system. Despite the advantages of the Hindu-Arabic numeral system in calculations, Roman numerals maintain a unique place in our culture and continue to serve various practical purposes. Their enduring legacy is a testament to their historical significance and lasting aesthetic appeal. Understanding Roman numerals not only enhances our comprehension of history but also adds to our appreciation of the diversity of numerical notation systems throughout time. From clock faces to copyright dates, Roman numerals offer a visual and historical richness that enhances the things they mark. Their elegant simplicity continues to be appreciated and utilized in a variety of modern applications.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is Li In Roman Numerals . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.