What Is Liv In Roman Numerals
News Co
Apr 05, 2025 · 5 min read
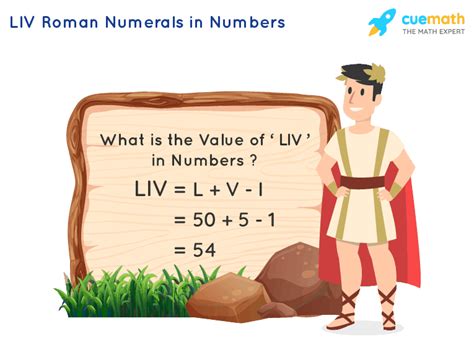
Table of Contents
What is LIV in Roman Numerals? A Deep Dive into Roman Numeral Systems
The question, "What is LIV in Roman numerals?" might seem simple at first glance. The answer, however, opens a door to a fascinating world of ancient numerical systems, their historical context, and the rules governing their interpretation. This comprehensive guide will not only answer the initial question but also explore the intricacies of Roman numerals, providing you with a thorough understanding of their structure, usage, and significance.
Understanding the Basics of Roman Numerals
Roman numerals are a numeral system that originated in ancient Rome and remained in use throughout the Roman Empire. Unlike the decimal system (base-10) we use today, which is based on powers of 10, Roman numerals employ a different approach using combinations of letters to represent numerical values. The system relies on seven basic symbols:
- I = 1
- V = 5
- X = 10
- L = 50
- C = 100
- D = 500
- M = 1000
These symbols, when arranged strategically, can represent any number. The key to understanding Roman numerals lies in grasping their additive and subtractive principles.
The Additive Principle
The additive principle is straightforward: smaller values placed to the left of a larger value are added to it. For example:
- XI = 10 + 1 = 11
- LX = 50 + 10 = 60
- CC = 100 + 100 = 200
This principle forms the foundation of Roman numeral representation, allowing for the construction of larger numbers through simple addition.
The Subtractive Principle
The subtractive principle introduces a layer of complexity. This rule states that when a smaller value is placed to the right of a larger value, it's subtracted from the larger value. This principle, while seemingly counterintuitive, enhances the efficiency of the system and avoids excessive repetition of symbols. Here are some examples:
- IV = 5 - 1 = 4
- IX = 10 - 1 = 9
- XL = 50 - 10 = 40
- XC = 100 - 10 = 90
- CD = 500 - 100 = 400
- CM = 1000 - 100 = 900
This principle is crucial for understanding why certain combinations of symbols result in specific values.
Decoding LIV: The Answer
Now, let's finally address the central question: What is LIV in Roman numerals?
Using our understanding of the additive and subtractive principles, we can break down LIV as follows:
- L = 50
- I = 1
- V = 5
Since I (1) is placed before V (5), we apply the subtractive principle: 5 - 1 = 4. Then, we add the value of L: 50 + 4 = 54.
Therefore, LIV in Roman numerals represents the number 54.
Advanced Aspects of Roman Numerals
While the basics are relatively simple, Roman numerals possess several nuances that enhance their versatility and demonstrate their elegance as a number system.
Limitations of Roman Numerals
Despite their historical importance, Roman numerals have limitations. They lack a concept of zero, making arithmetic operations involving zero impossible. Furthermore, performing complex mathematical calculations is significantly more challenging compared to using the decimal system. The absence of a placeholder for zero complicates calculations involving multiplication, division, and decimal fractions.
Variations and Conventions
Throughout history, there have been minor variations in the use of Roman numerals. While generally consistent, subtle differences can be found in different historical periods and geographical regions. Understanding these variations requires familiarity with the historical context of the specific Roman numeral inscription or manuscript being examined.
Modern Usage
Despite their limitations, Roman numerals continue to find applications in modern contexts. They are frequently seen in:
- Outlines: Organizing numbered points and subpoints in an organized structure.
- Clock faces: Displaying the hours on traditional analog clocks.
- Copyright dates: Indicating the year of copyright on publications and creative works.
- Monarch names: Identifying successive monarchs in a given lineage (e.g., King George V).
- Super Bowl numbering: Designating the annual Super Bowl game.
- Chapter numbering: In books and other written works.
These modern uses demonstrate the enduring appeal of Roman numerals, even within a world dominated by the decimal system.
Historical Context and Significance
The development of Roman numerals reflects the evolution of Roman society and its administrative structures. Their creation likely stemmed from the need for a standardized system for record-keeping, taxation, and governance. The symbols themselves may have evolved from earlier Etruscan numerical systems.
The longevity of Roman numerals speaks to their inherent usefulness and adaptability. Though surpassed by more efficient numerical systems for complex calculations, their concise and visually appealing nature has ensured their continued relevance and prevalence in various settings.
Beyond LIV: Exploring other Roman Numerals
Understanding LIV helps build a foundation for interpreting other, potentially more complex Roman numeral expressions. Let's explore a few examples:
- MCMXCIV (1994): This involves multiple subtractive and additive applications: M (1000) + CM (900) + XC (90) + IV (4).
- MMXXII (2022): A straightforward additive representation: MM (2000) + XX (20) + II (2).
- DCCCLXXXVIII (888): Demonstrates the additive principle with higher values: D (500) + CCC (300) + LXXX (80) + VIII (8).
By practicing the decomposition of these numbers, you strengthen your comprehension of the rules and principles governing Roman numeral representation.
Practical Exercises: Testing Your Understanding
To solidify your understanding of Roman numerals, try deciphering the following numbers:
- CLXVI
- DCCCXLV
- MDCCLXXVI
- CMXCIX
- DXCVIII
And then, try converting these numbers into Roman numerals:
- 1492
- 2789
- 567
- 999
- 345
Conclusion: The Enduring Legacy of Roman Numerals
The humble question of "What is LIV in Roman numerals?" has led us on a journey through the fascinating world of ancient numerical systems. We've uncovered the additive and subtractive principles that define Roman numeral representation, examined its historical context, and explored its continued relevance in modern usage. Roman numerals, despite their limitations, stand as a testament to the ingenuity of ancient civilizations and their lasting impact on our world. Hopefully, this in-depth exploration has not only answered your initial question but also provided a comprehensive understanding of this fascinating number system. Remember to practice and apply what you've learned to truly master the art of deciphering and utilizing Roman numerals.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is Liv In Roman Numerals . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.