What Is The Roman Numeral For 2000
News Co
Apr 12, 2025 · 4 min read
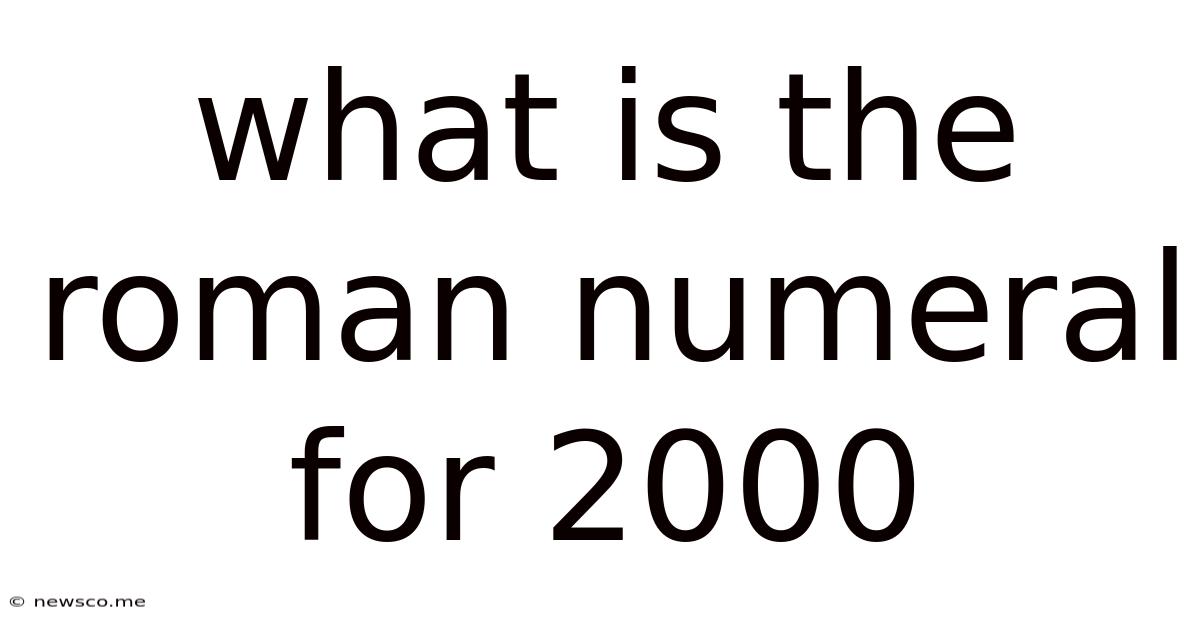
Table of Contents
What is the Roman Numeral for 2000? A Deep Dive into Roman Numerals
The question, "What is the Roman numeral for 2000?" seems simple enough. However, exploring this seemingly straightforward query opens a door to a fascinating world of ancient Roman mathematics and the evolution of numerical representation. This article will not only answer the question directly but also delve into the history, structure, and nuances of the Roman numeral system, equipping you with a comprehensive understanding of this enduring system.
Understanding Roman Numerals: A Historical Perspective
Roman numerals, a system of numerical notation used by the Romans, predate our modern decimal system. Their use spanned centuries, leaving an indelible mark on our culture and still finding application today, particularly in contexts like clock faces, chapter numbering in books, and copyright dates. Understanding their evolution helps us grasp their inherent complexities.
The Basic Symbols and Their Values
At the heart of the Roman numeral system are seven basic symbols:
- I: Represents 1
- V: Represents 5
- X: Represents 10
- L: Represents 50
- C: Represents 100
- D: Represents 500
- M: Represents 1000
These symbols, representing powers of 10 and their halfway points, form the foundation for constructing all other numbers.
The Additive and Subtractive Principles
The Roman numeral system employs two key principles for number construction:
- Additive Principle: Smaller values placed to the right of a larger value are added to it. For example, VI (5 + 1 = 6) and LXX (50 + 20 = 70).
- Subtractive Principle: A smaller value placed to the left of a larger value is subtracted from it. This is used for numbers like IV (5 - 1 = 4) and IX (10 - 1 = 9). Note that this subtractive principle is not applied indiscriminately; only certain subtractions are allowed (I before V or X, X before L or C, C before D or M).
These principles, combined with the seven basic symbols, provide the framework for representing a wide range of numbers.
The Roman Numeral for 2000: MM
Finally, let's address the central question: What is the Roman numeral for 2000? The answer is simply MM.
This is derived from the additive principle. Since M represents 1000, placing two Ms together (MM) represents 1000 + 1000 = 2000.
Beyond the Basics: Advanced Roman Numeral Concepts
While MM neatly solves our initial question, the Roman numeral system possesses complexities that warrant further exploration.
Larger Numbers and the Use of Vinculum
For numbers exceeding 3999, the Romans employed a technique called the vinculum. This is a bar placed above a numeral to multiply its value by 1000. For example:
- $\overline{V}$ = 5000
- $\overline{X}$ = 10000
- $\overline{L}$ = 50000
- $\overline{C}$ = 100000
- $\overline{D}$ = 500000
- $\overline{M}$ = 1000000
This system allowed the Romans to represent extremely large numbers, although its widespread use was less common compared to the basic system.
Variations and Inconsistencies
It is essential to acknowledge that the Roman numeral system wasn't always perfectly consistent throughout history and across different regions. Minor variations existed, reflecting the organic evolution of the system. These inconsistencies are rarely encountered today, as modern usage tends to adhere to a standardized form.
Roman Numerals in Modern Usage
Despite the rise of the Hindu-Arabic numeral system, Roman numerals continue to hold a place in contemporary society. They are frequently found in:
- Clock faces: Displaying the hours.
- Book chapters: Numbering chapters in books.
- Copyright dates: Indicating copyright years.
- Outlines and lists: Providing structured numbering.
- Formal documents: Adding a touch of traditional formality.
- Stone inscriptions and architectural markings: Perpetuating their historical presence.
Their persistence showcases their enduring appeal and their suitability for certain applications.
The Advantages and Disadvantages of Roman Numerals
Compared to the modern decimal system, Roman numerals offer both advantages and disadvantages:
Advantages:
- Simplicity of Basic Representation: The basic symbols are easy to learn and remember.
- Aesthetic Appeal: Their visual representation is often considered more elegant and traditional.
- Uniqueness: They offer a distinct visual identity, different from our everyday numbers.
Disadvantages:
- Lack of a Zero: The absence of a zero makes arithmetic operations, especially subtraction and division, more challenging.
- Inefficiency for Large Numbers: Representing large numbers becomes cumbersome and requires more symbols.
- Ambiguity with the Subtractive Principle: The subtractive principle requires careful attention to avoid misinterpretations.
- Limited Applicability for complex mathematical operations: Their structure doesn't lend itself easily to advanced arithmetic.
Roman Numerals and Modern Mathematics
While Roman numerals are not suited for complex calculations or large-scale numerical work, understanding them provides valuable insights into the history of mathematics. Their limitations highlight the advantages of the modern decimal system, particularly in efficiency and applicability. The historical context of Roman numerals adds depth and richness to our understanding of number systems and their evolution.
Conclusion: MM and the Enduring Legacy of Roman Numerals
The Roman numeral for 2000, MM, is a simple yet representative example of this system. This seemingly straightforward answer opens up a broader conversation about the historical context, structure, and limitations of Roman numerals. Though our modern decimal system has largely replaced Roman numerals in everyday calculations, their presence in contemporary society and their historical significance remain undeniable. Their elegance and historical significance ensure their continued use and study, serving as a testament to the enduring legacy of Roman civilization. Understanding Roman numerals offers a glimpse into a rich mathematical past, enriching our appreciation for the evolution of numerical systems and the ingenious systems devised by past civilizations.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Roman Numeral For 2000 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.