What Is Xxviii In Roman Numerals
News Co
Apr 04, 2025 · 5 min read
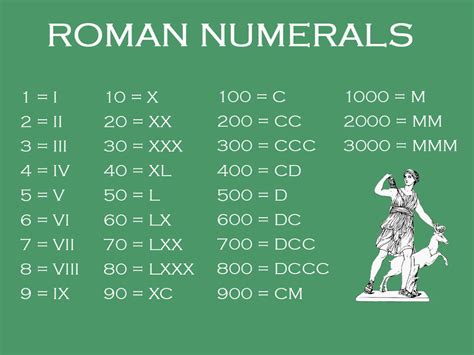
Table of Contents
What is XXVIII in Roman Numerals? A Deep Dive into Roman Numeral System
Understanding Roman numerals might seem like a journey back in time, but their presence continues to linger in various aspects of modern life. From chapter numbering in books to clock faces and copyright dates, Roman numerals remain a recognizable, albeit somewhat enigmatic, system. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of Roman numerals, focusing specifically on XXVIII, explaining its meaning, the rules governing the system, and offering practical applications to solidify your understanding.
Deciphering XXVIII: Unlocking the Roman Numeral Code
XXVIII represents the number 28 in the Roman numeral system. Let's break down how this representation is derived:
- X: Represents 10. The numeral X appears twice in XXVIII (XX), signifying 10 + 10 = 20.
- V: Represents 5. This is added directly to the existing sum.
- I: Represents 1. The numeral I appears three times (III) representing 1 + 1 + 1 = 3.
Therefore, adding these values together (20 + 5 + 3) gives us the final answer: 28.
The Fundamentals of the Roman Numeral System: A Comprehensive Guide
The Roman numeral system is based on a combination of seven basic symbols:
- I: 1
- V: 5
- X: 10
- L: 50
- C: 100
- D: 500
- M: 1000
These symbols can be combined to represent larger numbers. The key to understanding the system lies in its rules of combination and placement:
Additive Principle:
When a smaller numeral is placed to the right of a larger numeral, it is added. For example:
- VI: 6 (V + I)
- XI: 11 (X + I)
- LX: 60 (L + X)
Subtractive Principle:
This is where the system gets a little more nuanced. When a smaller numeral is placed to the left of a larger numeral, it is subtracted. This rule applies only to the following specific combinations:
- IV: 4 (5 - 1)
- IX: 9 (10 - 1)
- XL: 40 (50 - 10)
- XC: 90 (100 - 10)
- CD: 400 (500 - 100)
- CM: 900 (1000 - 100)
This subtractive principle enhances the efficiency of the system, avoiding the need for lengthy strings of repeated symbols.
Limitations of the Roman Numeral System:
While elegant in its simplicity, the Roman numeral system does possess certain limitations:
- No concept of zero: The Romans did not have a symbol for zero.
- Limited use for large numbers: Representing exceedingly large numbers becomes cumbersome.
- Lack of standardized notation: Historically, different variations existed, leading to potential ambiguity. Modern conventions have largely standardized the system.
- No arithmetic operations: The system is primarily for representing numbers, not for performing calculations.
Practical Applications of Roman Numerals: Beyond the Classroom
Despite its limitations, Roman numerals retain a surprising relevance in contemporary life. Here are some common areas where you'll encounter them:
- Clock faces: Many analog clocks use Roman numerals for the hours (typically I through XII).
- Outlines and chapter numbering: Books and academic papers often employ Roman numerals for outlining main sections or numbering chapters.
- Copyright dates: Copyright information sometimes includes Roman numerals, adding a touch of formality.
- Formal documents: Roman numerals are sometimes used in formal documents to represent sequential numbering or ordinal numbers (e.g., King George VI).
- Architectural design: Roman numerals are often integrated into architectural elements for numbering floors, buildings, or decorative purposes.
- Calendars and historical timelines: They can add a visually appealing aesthetic to these displays.
Understanding Roman numerals, therefore, extends beyond mere historical curiosity; it’s a practical skill with ongoing applications.
Beyond XXVIII: Exploring Higher Roman Numerals
Let’s build on our understanding of XXVIII and explore how to represent larger numbers using the Roman numeral system:
- XXIX: 29 (XX + IX)
- XXX: 30 (XXX)
- XXXIX: 39 (XXX + IX)
- XL: 40 (50 - 10)
- L: 50
- LX: 60 (L + X)
- LXX: 70 (L + XX)
- LXXX: 80 (L + XXX)
- XC: 90 (100 - 10)
- C: 100
- CC: 200 (C + C)
- CCC: 300 (C + C + C)
- CD: 400 (500 - 100)
- D: 500
- DC: 600 (D + C)
- DCC: 700 (D + CC)
- DCCC: 800 (D + CCC)
- CM: 900 (1000 - 100)
- M: 1000
- MM: 2000 (M + M)
- MMM: 3000 (M + M + M)
- MMMM: 4000 (Although technically correct, overline notation becomes preferred for larger numbers, representing 4000 as $\overline{IV}$ )
The use of overlines (vinculum) to denote multiplication by 1000 is a standard practice for very large numerals. For example:
- $\overline{V}$: 5000
- $\overline{X}$: 10,000
- $\overline{L}$: 50,000
- $\overline{C}$: 100,000
- $\overline{D}$: 500,000
- $\overline{M}$: 1,000,000
Mastering Roman Numerals: Practice Exercises
To reinforce your understanding, try converting the following numbers into Roman numerals:
- 17
- 35
- 62
- 88
- 199
- 444
- 999
- 1234
And convert these Roman numerals to Arabic numbers:
- XIV
- LIX
- CXXVIII
- CDXCIX
- MMMDCCCLXXXVIII
Conclusion: Embracing the Timeless Elegance of Roman Numerals
The Roman numeral system, despite its age, continues to hold a significant place in our world. Understanding its underlying principles – the additive and subtractive principles – unlocks the ability to decipher and utilize this ancient yet enduring system. Whether you encounter it on a clock face, in a book, or in a historical context, your newfound knowledge will allow you to appreciate the elegance and practicality of Roman numerals. With practice and a little bit of understanding, the seemingly cryptic world of Roman numerals will become clear and accessible. So, the next time you see XXVIII, you'll know exactly what it means and how it fits within the fascinating history and ongoing usage of this remarkable numerical system.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is Xxviii In Roman Numerals . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.