X X X I I I Roman Numerals
News Co
Apr 15, 2025 · 5 min read
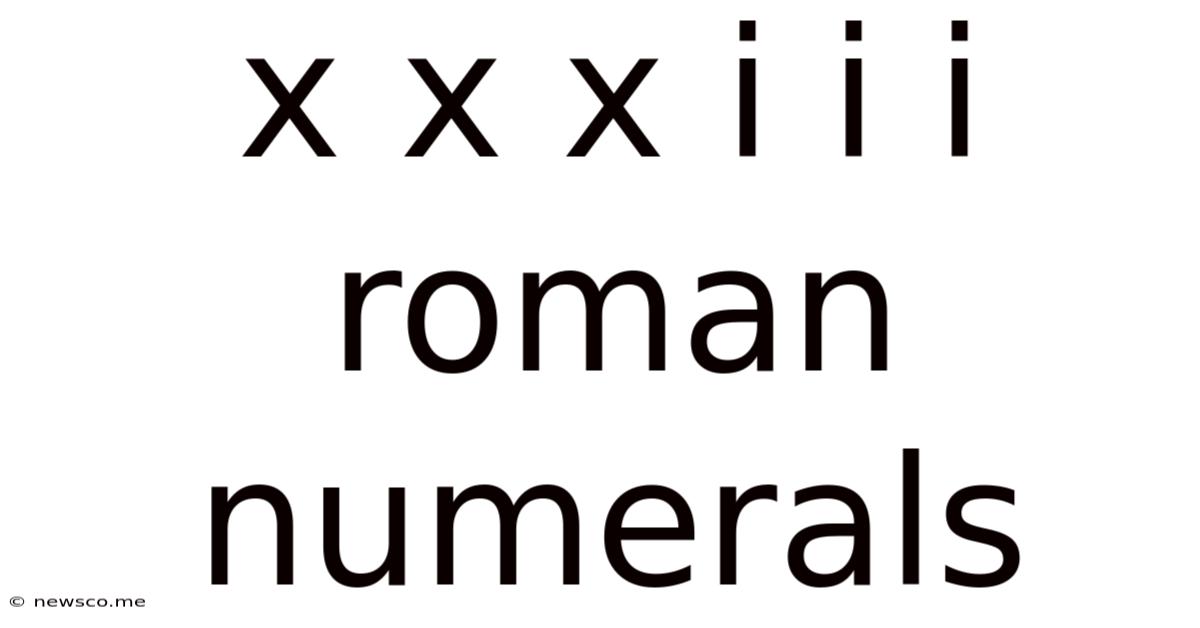
Table of Contents
Decoding the Mystery: A Deep Dive into XXX III III Roman Numerals
Roman numerals, a system of numerical notation originating in ancient Rome, continue to fascinate and intrigue. While largely replaced by the more efficient Hindu-Arabic numeral system in most contexts, Roman numerals persist in various applications, from clock faces and chapter headings to copyright dates and outlines. Understanding their intricacies offers a glimpse into history and a unique appreciation for a less intuitive yet elegant numbering system. This article delves deep into the representation and interpretation of XXX III III, exploring its composition, variations, and significance within the broader context of Roman numerals.
Understanding the Basics of Roman Numerals
Before dissecting XXX III III, let's establish a foundational understanding of how Roman numerals work. The system utilizes seven basic symbols:
- I: Represents 1
- V: Represents 5
- X: Represents 10
- L: Represents 50
- C: Represents 100
- D: Represents 500
- M: Represents 1000
These symbols are combined to represent larger numbers. The key principle is the additive and subtractive nature of the system. Additive means placing symbols in descending order to add their values (e.g., VI = 6, XV = 15). Subtractive, however, involves placing a smaller value symbol before a larger one to subtract the smaller value from the larger (e.g., IV = 4, IX = 9).
Important Considerations:
- Repetition: A symbol can be repeated up to three times consecutively (e.g., III = 3, XXX = 30). Repeating a symbol more than three times is not standard Roman numeral practice.
- Subtraction Limitations: Subtraction is generally limited to a single smaller numeral preceding a larger numeral. You won't see things like IIX or IXIV.
- Specific Patterns: Certain combinations are more prevalent than others. For example, you'll more often see combinations utilizing the subtractive principle for numbers like 4 (IV) and 9 (IX) rather than their additive counterparts (IIII and VIIII). This convention improves readability and avoids ambiguity.
Decomposing XXX III III: A Step-by-Step Analysis
Now, let's analyze the specific Roman numeral expression: XXX III III. Breaking it down piece-by-piece clarifies its meaning:
- XXX: This represents 30. The symbol X is repeated three times, demonstrating the additive principle. 3 x 10 = 30.
- III: This represents 3. The symbol I is repeated three times, again utilizing the additive principle. 3 x 1 = 3
- III: This also represents 3. Identical to the previous instance.
Therefore, adding the values together: 30 + 3 + 3 = 36.
XXX III III = 36
This demonstrates a straightforward application of the additive principle within the Roman numeral system. No subtractive elements are present in this particular combination.
Variations and Contextual Understanding
While XXX III III directly translates to 36, it's crucial to consider that the presentation of Roman numerals can sometimes vary depending on the context or historical period. Although this variation is less common in modern usage, understanding these potential differences ensures accurate interpretation.
For example, in some historical inscriptions or less formal representations, variations might have been employed. However, the standard and most widely accepted representation remains consistent with the additive principles discussed earlier. The modern convention prioritizes clarity and standardization to avoid confusion.
Why Use Roman Numerals? Applications and Persistence
Given the simplicity and efficiency of the Hindu-Arabic numeral system, the continued presence of Roman numerals warrants examination. Their persistence stems from various factors:
- Tradition and Aesthetics: Roman numerals often convey a sense of tradition, formality, and elegance. Their use in clock faces, chapter headings, and copyright notices often contributes to a sophisticated aesthetic.
- Historical Significance: Roman numerals maintain a connection to the Roman Empire and its enduring influence on Western civilization. Their use helps preserve a link to history.
- Specific Applications: In certain specialized contexts, Roman numerals remain practical or even preferable. For example, outlining sections in formal documents or denoting specific ordinal numbers (e.g., King Henry VIII) retains a traditional clarity.
- Avoiding Ambiguity with Ordinal Numbers: Roman numerals are naturally suited to represent ordinal numbers, reducing the potential for confusion. Consider the difference between "Chapter 1" and "Chapter I" – the Roman numeral version clearly denotes it's an ordinal.
Advanced Roman Numerals: Exploring Numbers Beyond 1000
While the basic symbols handle numbers up to 1000, representing larger numbers requires specific conventions:
- Overlining: Placing a bar above a numeral multiplies its value by 1000. For example, $\overline{X}$ represents 10,000, and $\overline{M}$ represents 1,000,000.
- Combining Symbols: Larger numbers are formed by creatively combining basic symbols. For example, MCMXCIX represents 1999.
Understanding these advanced conventions enables interpreting increasingly complex Roman numeral representations.
Roman Numerals and Modern Technology
Interestingly, Roman numerals have found their way into modern technological applications. While not widely used for computations, their unique aesthetic properties are often leveraged:
- Software Design: Some software interfaces utilize Roman numerals for visual appeal or to denote versions or iterations.
- Gaming: Video games sometimes employ Roman numerals for a thematic or historical effect, adding a stylistic touch.
- Website Design: Roman numerals can be incorporated into website design elements to create a distinctive look and feel.
Common Misconceptions about Roman Numerals
Several common misconceptions surround the Roman numeral system:
- Unlimited Repetition: While repetition is allowed, it's limited to a maximum of three consecutive repetitions of the same symbol.
- Arbitrary Symbol Combination: The order of symbols follows specific rules, adhering to the additive and subtractive principles. Random combinations don't necessarily represent valid numbers.
- Modern Flexibility: While certain modern variations exist, the core principles of the system remain consistent, promoting standardization and readability.
The Enduring Legacy of Roman Numerals
In conclusion, XXX III III, representing 36, serves as a simple yet illustrative example of the Roman numeral system. While the Hindu-Arabic system prevails in most mathematical and scientific contexts, the enduring legacy of Roman numerals is evident in their continued usage across various applications. Their aesthetic appeal, historical significance, and specific practical applications ensure their continued presence, offering a unique glimpse into the past while maintaining a place in the modern world. Understanding their structure and principles allows us to appreciate the elegance and complexity hidden within these seemingly simple symbols, revealing a system that has transcended centuries. The continued use of Roman numerals demonstrates their enduring appeal and the inherent human fascination with the systems and symbols that shape our understanding of quantity and number. Whether appearing on a clock face, a historical inscription, or a modern software interface, Roman numerals continue to leave their mark on our world.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about X X X I I I Roman Numerals . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.